In order to understand the importance of the participation of each and every voter in the legislative elections, it is necessary to understand what competences the Constitution of the Portuguese Republic (CRP) has assigned to the Portuguese Parliament.
Before we go any further, it should be noted that the Portuguese Parliament (AR – Assembleia da República) is one of the four State’s sovereign bodies (Article 110 of the CRP), but political power belongs to the people (Article 108 of the CRP). Part III of the CRP, entitled “Organisation of Political Power”, contains Title III dedicated to the AR, which is defined as the representative assembly of all Portuguese citizens (Article 147 of the CRP).
As we have seen in this post, the AR is currently made up of 230 Members (Article 148 of the CRP), who are elected by direct and secret universal suffrage, as we have seen in this other post.
As for the AR’s constitutional duties, and as its website explains, the main competences are to legislate and supervise the actions of the Government. Thus, the AR has political and legislative competence (Article 161 of the CRP), supervisory competence (Article 162 of the CRP), and competence over other bodies (Article 163, CRP).
Therefore, one of the AR’s main functions is to legislate, and it can make laws on all matters, except those reserved by the Constitution for the Government (Article 161(c) of the CRP). In addition, the ability to present projects or proposals for laws (legislative initiative) can be exercised by:
- Members of Parliament and parliamentary groups (legislative project);
- Groups of voting citizens, under the terms of Law no. 17/2003, of 4th June, in its current wording;
- The Government and the Regional Legislative Assemblies (legislative proposal).
See the chart below drawn up by the Portuguese Parliament to understand how a law is made:

Source: Portuguese Parliament
Para que possamos compreender a importância da participação de cada um/a dos/as eleitores/as nas eleições legislativas, faz-se necessário perceber quais são as competências que a Constituição da República Portuguesa (CRP) atribuiu à Assembleia da República.
Antes de avançarmos, destaca-se que a Assembleia da República (AR) é um dos quatro órgãos de soberania do Estado (art. 110.º, CRP), mas o poder político pertence ao povo (art. 108.º, CRP). Na Parte III da CRP, intitulada “Organização do Poder Político”, encontraremos o Título III dedicado à AR, que é definida como a assembleia representativa de todos/as os/as cidadãos/ãs portugueses/as (art. 147.º, CRP).
Como vimos nesta publicação, a AR é composta atualmente por 230 Deputados (art. 148.º, CRP), que são eleitos por sufrágio universal direto e secreto, como vimos nesta outra publicação.
Quanto às atribuições constitucionais da AR, e conforme explica o seu website, as “principais competências são legislar e fiscalizar a atuação do Governo“. Assim, a AR tem competência política e legislativa (art. 161.º, CRP), competência de fiscalização (art. 162.º, CRP), e competência quanto a outros órgãos (art. 163.º, CRP).
Portanto, uma das principais funções da AR é legislar, podendo fazer leis sobre todas as matérias, salvo as reservadas pela Constituição ao Governo (art. 161.º, al. c), da CRP). Ainda,a capacidade de apresentar projetos ou propostas de lei (iniciativa legislativa) pode ser exercida por:
- Deputados e grupos parlamentares (projetos de lei);
- Grupos de cidadãos eleitores, nos termos da Lei n.º 17/2003, de 04 de junho, na sua redação atual;
- Governo e Assembleias Legislativas Regionais (propostas de lei).
Veja o quado abaixo elaborado pela Assembleia da República para compreender a feitura de uma lei:
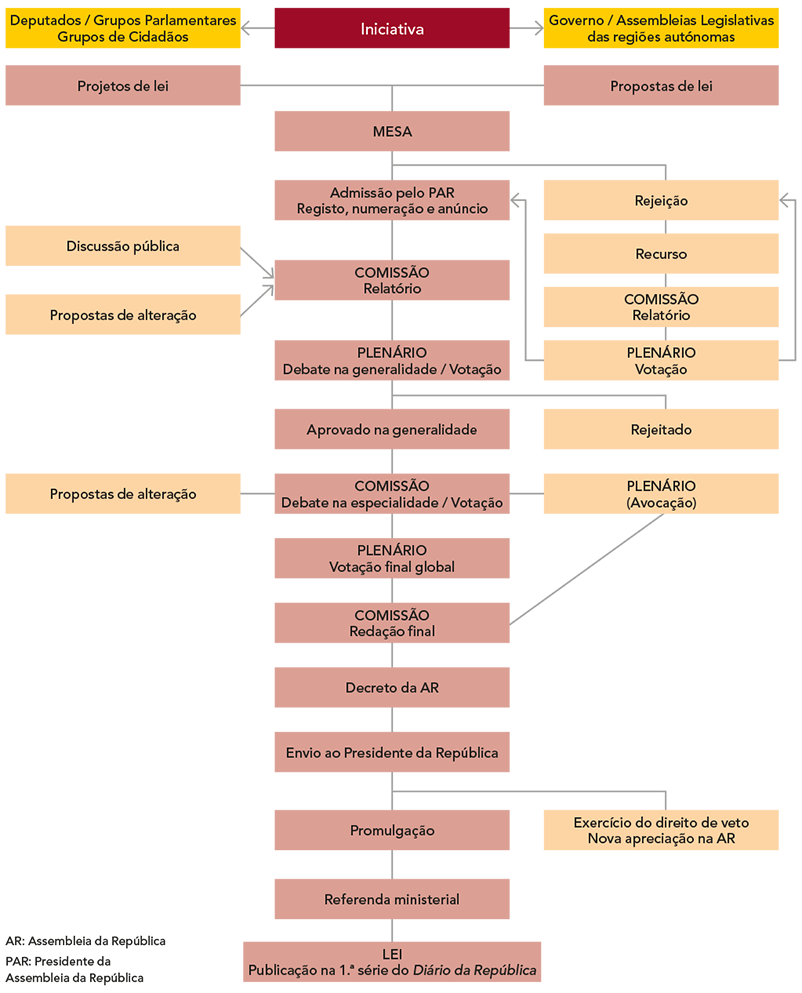
Fonte: Assembleia da República – Como se faz uma Lei? | Parlamentês
Project Team | Equipa do Projeto:
Emellin de Oliveira & Ana Cansado
Project Duration | Duração do projeto:
From December/23 to June/24 - De dezembro/23 a junho/24
